Keyboard Shortcuts - Moved to Keyboard Shortcuts | Everdo Help
Everdo relies heavily on keyboard shortcuts to achieve fast and low-friction user experience.
Item Creation
| key | action |
|---|---|
i |
Create an Inbox item |
n |
Create New item in the current view |
p |
Create a Project |
b |
Create a noteBook |
Navigation and Quick Editing
| key | action |
|---|---|
j |
select next item |
down |
select next item |
k |
select previous item |
up |
select previous item |
enter |
open item editor |
alt + enter |
open corresponding project |
f |
toggle focus selected item |
space |
toggle complete selected item |
d |
toggle due date for selected item |
x |
move item to trash |
[ |
collapse item description [1.2.6+] |
] |
expand item description [1.2.6+] |
Alt+[ |
collapse all items in view [1.2.6+] |
Alt+] |
expand all items in view [1.2.6+] |
Sidebar Navigation
| key | action |
|---|---|
1 |
Inbox |
2 |
Next |
| … | |
0 |
Trash |
Areas
| key | action |
|---|---|
Shift + 0 |
All Areas |
Shift + 1 |
Area 1 |
| … | |
Shift+0 |
Unassigned items |
Misc Shortcuts
| key | action |
|---|---|
h |
Open Help |
t |
Open Tag manager |
s or /
|
Search all items (non-archived, non-deleted) |
Save / Cancel Conventions
- “Escape” cancels changes and closes dialogs instantly without asking questions
- “Enter” or “Ctrl+Enter” saves and closes the current editor/dialog
← Back to Contents
Inline Commands - Moved to https://help.everdo.net/docs/features/commands
Inline commands allow to modify item’s properties simply by editing it’s title:
Commands can be applied when creating a new item or editing an existing item.
You can also quickly activate the command entry mode by pressing : on the keyboard.
To apply an inline command, type it at the end of the item’s title and press Save or “Enter”.
You can combine multiple commands. For example, setting the focus, high energy and due date could be done as follows:
:f :e high :d
Once applied, the commands are removed from the title. Invalid or non-recognized commands will stay in the title as text.
Available Commands
| command | example | app version |
|---|---|---|
| move to next | :n |
|
| move to someday/maybe | :m |
|
| move to scheduled and set start date | :s |
|
| move to waiting | :w |
v1.2.16+ |
| move to waiting and set contact | :w Name |
v1.2.16+ |
| move to projects | :p |
v1.2.16+ |
| set start date to tomorrow | :s |
|
| set start date to n days in the future |
:s 5 |
|
:s 5d |
||
| set specific start date | :s May 5 |
|
:s 5 May |
||
:s 5 May 2018 |
||
| focus item | :f |
|
| remove focus | :f none |
|
| set time in minutes | :t 10m |
|
:t 10 |
||
| set time in hours | :t 1h |
|
| remove time estimate | :t none |
|
| set energy to High | :e h |
|
:e high |
||
| set energy to Medium | :e m |
|
:e med |
||
| set energy to Low | :e l |
|
:e low |
||
| remove energy estimate | :e none |
|
| set due date for Today | :d |
|
| set due date n days in the future/past | :d +5 |
|
:d 5 |
||
:d -1 |
||
| set specific due date | :d May 5 |
|
:d 5 May |
||
:d 5 May 2018 |
← Back to Contents
Search - Moved to Search | Everdo Help
To search items you can use the search textbox at the top of Everdo window:
By default, search works across all items that are:
- not archived
- not in trash
The following item properties are matched against the search query:
- title
- note/description
Search Shortcuts
- To quickly initiate search: press
sor/, then type your query - To cancel search: press
esc
Advanced Search Options
You can change the scope of search by specifying a search operator at the beginning of your query:
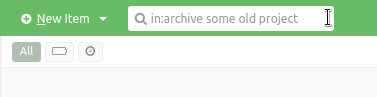
| scope of search | search query |
|---|---|
| archived items | in:archive |
← Back to Contents
Export - Moved to Exporting Data | Everdo Help
Everdo offers several ways get your data out of the app for analysis, reporting, backup or other reasons.
- Copy as Text
- CSV Export
- JSON Export
- Direct database access
Copy as Text
This feature is useful to quickly get the contexts of the current view/list in a human-readable plain text format:
Next
----
[ ] Try using "Export as CSV"
[ ] Try using "Export as JSON"
Done
----
[x](Apr 2) Use "Copy as Text"
To make the export :
- Click “Copy as Text” button in the filter bar
- Paste into to a text editor
JSON Export
JSON export allows to get the complete data in a machine-friendly format well suited for further automated processing.
CSV Export
This feature allows to export all Everdo data in a standard format readable by Excel and other spreadsheet programs.
Direct Database Access
 Always use a copy, not the actual Everdo
Always use a copy, not the actual Everdo db file. Never modify the database file directly. It’s very easy to change data in such a way that will lead to Everdo crashing.
All the Everdo data is stored in a single sqlite database file, located in the Everdo application directory. You can copy the database file and use the copy to extract and analyze your data.
← Back to Contents
Encrypted Sync Service (ESS) - Moved to Encrypted Sync Service | Everdo Help
Encrypted Sync Service is the easiest way to sync your Everdo data between your devices.
How it works
ESS sync works similarly to the network-based sync. The differences are:
- You don’t host the server yourself, which makes configuration easier and you don’t have to rely on a specific physical network for it to work smoothly.
- All text data transmitted for sync purposes gets client-side encrypted. The sync server never receives or stores clear text.
Each of your devices needs to have the same encryption passphrase set up to be able to work with encrypted data.
Before you begin
- It’s highly recommended that you backup your Everdo database. Backing up is easy and is a good practice, especially when using beta functionality.
- Make sure Everdo version is at least 1.2.0 on your computers and 0.76.2 on Android devices.
Step 1: Create ESS Account
Open Everdo on your computer and go to Settings (Ctrl+,). Open “Sync” tab select “Encrypted Sync”, then “Get Sync Account”.
Fill in the sign-up form that opens in your browser:

You will receive a confirmation email with a link to activate the account. Once activated, you’ll see your subscription status displayed as “Active” on the web page:

Step 2: Setup Encrypted Sync on Desktop
 Important: at the end of setting up a device, don’t forget to click the Push button to ensure all existing items and tags from that device get added to ESS. Otherwise syncing may be incomplete, resulting in missing tags, projects and so on.
Important: at the end of setting up a device, don’t forget to click the Push button to ensure all existing items and tags from that device get added to ESS. Otherwise syncing may be incomplete, resulting in missing tags, projects and so on.
Use the ESS account you created in Step 1 to sign in on your computer:

Once signed in, a random 16-word passphrase will be generated for you to serve as an encryption key (see the image below). You can view the passphrase as text or QR code. It’s also possible to generate a new one. You don’t need to remember or even store this passphrase - you only need to transfer it to your other devices.
If you would like to set your own passphrase, or transfer a passphrase from another device, you may edit the text field manually. If you choose to generate your own passphrase outside of Everdo, make sure that it contains 16 random English words from a large dictionary.

You should now see the sync status updating at the bottom of the settings window.
 Important: now you need to click the Push button to ensure all existing items and tags from that device get added to ESS. Otherwise syncing may be incomplete, resulting in missing tags, projects and so on.
Important: now you need to click the Push button to ensure all existing items and tags from that device get added to ESS. Otherwise syncing may be incomplete, resulting in missing tags, projects and so on.

Now press “Apply” to save the configuration and you are done.
Step 3: Android App and Other Computers
Once you have one computer configured, the rest is easy. To setup other computers follow the same instructions as in Step 2, only this time use the existing ESS account and encryption key instead of creating new ones.
To setup an Android device, go to Everdo Settings on the phone and update the Sync Settings accordingly. You’ll need to sign in and specify the encryption key, same as you did on Desktop. When it comes to entering the encryption key, it might be easier to scan the QR code from the computer instead of entering the text manually. Don’t worry, you only need to do this once.
After you’ve specified all the sync settings, go back to the app and swipe down to trigger sync and ensure it’s working. Once you see sync working, you can enable auto-sync in Settings.
Making sure the same encryption key is used on all devices
As mentioned before, each of your devices should be set up with the exact same encryption key.
Otherwise they would not understand each other’s data and sync wouldn’t work.
To make sure this requirement is met, ESS is capable of detecting when different devices are using different keys.
In such scenario ESS will refuse to sync the device who’s key doesn’t match. This will be reflected as a warning in the sync settings dialog.
Proxy server settings
To specify a proxy server for ESS calls, specify proxy in the configuration file as follows (1.2.19+ only).
{
...
"proxy": "http://user:password@1.2.3.4:12345"
}
Alternatively, use an environment variable PROXY. The proxy setting will be displayed it in the ESS configuration dialog, if specified.
Manual Sync Actions
There are several actions that you can manually trigger in the settings dialog if necessary to reconcile a data discrepancy between devices caused by a bug, changing sync settings and so on. Before using these actions it’s important to understand how they work to avoid unexpected results.
First, let us understand how the automatic sync works. It’s important to understand that autosync is incremental, which means that your whole database is not being transmitted every time something changes. Instead, only the actual change get synced. This is why it’s important to Push data to ESS when transitioning from network sync - otherwise Everdo will only send incremental updates, while ESS still doesn’t have any existing data to apply the updates to!
Now to manual actions.
Push - this will copy all items and tags from the device L to ESS E, making ESS data after the push (E') completely match the local data. This action will completely discard the original ESS data.
E'(L, E) = L
Force Push - same logic as push, but force ESS to accept data encrypted with a new key. This action will make other devices unable to sync until you configure them with the new encryption key.
Pull - copy all items and tags from ESS to the local database, overwriting any conflicts. After the pull, the local data L' may be different from ESS because it can still contain items not previously synced to ESS.
L'(L, E) = L union E
Clean Pull (1.2.7+) - import all items and tags from ESS (E) into an empty local database. This can be used to make the state on the device exactly identical to the ESS. WARNING: Items that have not been previously synced/pushed to ESS will be lost because the original local data L is discarded in favor of ESS data E.
L'(L, E) = E
Be careful when doing Clean Pull- there is a scenario when data loss is possible. If you used network sync before and then configured ESS, but forgot to make an initial Push, then making a Clean Pull will remove all your local data and import everything from ESS. But there may yet be no data in ESS! This is simply because incremental sync only sends incremental changes, so ESS doesn’t have all your old, previously synced data.
Q&A
Once I start using ESS, can I go back to network sync?
Yes. It’s just a matter of re-configuring your devices.
Which data gets encrypted and how?
The titles and descriptions of items and tags are encrypted with AES256-CBC.
A 16-word passphrase generated on your computer is used as the encryption key. The passphrase is stored on each synced device in order to work with the encrypted data (but not on ESS server).
Each string gets encrypted separately for every sync attempt and gets it’s own IV.
This is what an action’s title looks like when encrypted: 1.EoCd6AP5LeGP937S3Mi31g==.kFdPOGCP7e+Z8sAl4wcesADJY54TQULqmmUETq2QWHY=
Is my data also stored in an encrypted form on my devices?
No, the data on you devices is still in clear text. It’s only encrypted prior to being sent to ESS. Doesn’t make sense to store encrypted data on your own device since the key is stored in the same place anyway.
What happens if I lose the encryption key?
The encryption key is stored in a text file on your computer in the same directory as the Everdo database. If you lose it somehow, it’s not a huge problem, since the data is still stored unencrypted on each of your devices. You can simply generate a new encryption key, update all devices to use it, then use the “Force Push” function to tell ESS to accept the new key, despite the mismatch.
I’m getting the “Key Mismatch” error
This means the device your are currently trying to sync uses a different encryption key compared to the one seen by ESS previously. You need to set the encryption keys to be exactly the same on all devices.
← Back to Contents
Backing Up Everdo Database - Moved to Data Directory | Everdo Help
Sqlite file backup (recommended)
The database file is located at the following location depending on your platform:
- on Linux: ~/.config/everdo/db
- on MacOS: ~/Library/Application Support/everdo/db
- on Windows: %USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\Everdo\db
To make a backup, copy the db file to another location. To restore a backup, replace the db file and restart Everdo.
JSON Export Backup
Alternatively, you could make a JSON export from within Everdo. Restore by importing the file. This way of backing up keeps your data safe, but it doesn’t preserve sync metadata.
← Back to Contents
Scheduling, Repeating Actions, Due Dates - Moved to Scheduling | Everdo Help
There are two ways to schedule an action in Everdo:
- Set a start date (defer)
- Make repeating
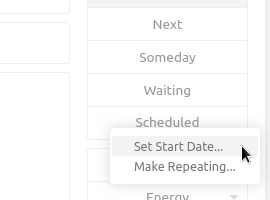
Set Start Date / Defer Action
Setting a start date is meant to defer an action or a project, “hiding” it until a specific date. Once the start date is set, the item gets moved to Scheduled until the specified date comes. Once the start date arrives, Everdo automatically moves the action/project to Next and makes it focused (starred).
Repeating Actions
The other scheduling option is to make an action repeating. This works a bit differently. Once an action is made Repeating, it gets moved to Scheduled, same as when setting a start date:
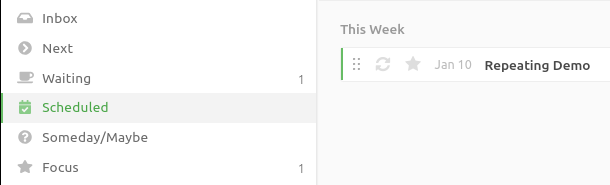
But once the time comes to repeat the action, it gets copied to Next (not moved). The original action stays in Scheduled, unchanged. In other words, the scheduled item serves as a template for further repeating clones.
Once a clone action is made, you can modify/complete/delete it, which will not affect the original (template) action.
To stop the action from repeating, you’ll need to remove or archive the template scheduled action.
Here’s a picture to illustrate how the action shown above got copied to Next and focused automatically. Notice the difference in the appearance (icons) between the template and the clone:
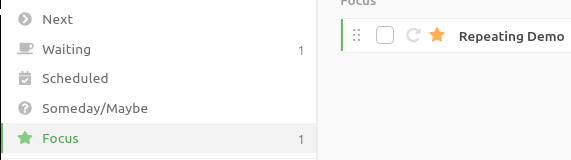
A new clone action gets created every time according to the schedule specified in the original template action.
Due Dates (Deadlines)
To avoid confusion, please note that the concept of a due date in Everdo is completely separate from Scheduling/Repeating. In other words, you can have a Next action with or without a due date, or you can have a Scheduled action with or without a due date. You can even assign a due date to an item still in Inbox.
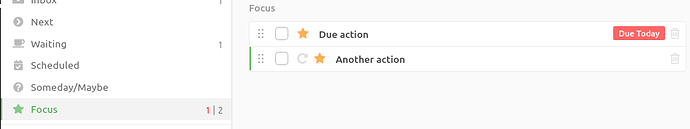
So what does it mean that an action has a due date? In Everdo it means that when the date comes, the action will automatically be Focused (starred) with no way to manually unfocus. The goal is to draw your attention and make the due date difficult to miss:
The picture shows two focused actions, one of which has a due date set for today. This makes the action stand out, even in the Focus view.
To set/change a due date, you can use the button at the bottom of the item editor:
Misc Notes
- Both Actions and Projects can have a start date
- Only Actions can be made Repeating
- You can quickly set start date and due date via inline commands
← Back to Contents
Tags: Labels, Areas, Contacts, Contexts - Moved to Tags | Everdo Help
Each item in Everdo can be assigned a set of tags.
There are three basic types of tags, each serving a different purpose:
- Label - the most basic type, can be used to filter items in the current view
- Area - similar to Label, but can also work as a global application-level filter
- Contact - can be assigned to items on the Waiting list to specify the person you are waiting for
Using Labels
You can use labels to “mark” your actions and projects in a way that makes it easier for you to find relevant work later. Some examples of using labels:
- priority labels (“p1”, “p2”, “p3”)
- work type labels (“writing”, “coding”, “chores”, “call”, etc)
- contextual labels ("@store", “@computer”, “@review”)
When coming up with labels, make sure they are actually useful for you as filters later. Otherwise you’ll just spend time labeling everything for no benefit.
Using Areas
Areas are most useful as a way to separate your different areas of focus or areas of expertise. Once you select a global area filter at the top of Everdo window, you will only see the items related to that area. This will help keep you GTD lists relevant and manageable:
You can transform an existing Label into an Area. Open the tag management window by pressing T, find the tag you would like to transform, then change it’s type to Area. As soon as you do this, the Area will be added to the area selector menu.
Context Tags
If you name any tag so that it starts with “@”, The tag will also appear in the Contexts section of the navigation pane. This will make it more convenient to view the associated items and let you drag-and-drop items “into” the contexts.
Any type of tag can be made a context by adding the “@” at the beginning - so for example you can have an Area tag that also appear in Contexts.
Misc Notes
- Project actions inherit the tags assigned to their parent project
- To rename/delete tags, press T
- To change a tag’s color, right-click on the tag anywhere in the app
- The only way to create a new tag is to assign it to an Item (you can’t create a tag that’s not assigned to anything)
- Deleting a tag will remove it from all items (both active and archived) with no way to undelete
← Back to Contents
Filtering - Moved to Filtering | Everdo Help
You can filter items in the current view by various properties:
- time
- energy
- tag assigned
- due date
All chosen filters get combined with logical AND, meaning that by selecting a set of filters you are reducing the set of visible items to the ones that satisfy every filter in the set
Filtering by multiple tags and “negative” filtering
It’s possible to filter the current view by any number of tags which appear in the filter bar:
To include items with a certain tag, left-click that tag in the filter bar. To exclude items with a certain tag, right-click that tag. For multiple selection hold Ctrl.
The tag filters get combined by logical AND for example if you have selected tag1, tag2 and tag3
On Mobile
The logic of filtering is the same, but to select multiple tags you simply tap each one. To negate, long-tap.
← Back to Contents
Projects - Moved to Projects | Everdo Help
According to GTD, a project is an outcome or an objective. It’s different from an action in that a project typically can’t be completed “in one sitting” because it requires more planning and will likely involve multiple actions. An action, on the other hand, is something you can just start and finish when you get to it.
The fastest way to create a project in Everdo is by pressing P.
Project actions
A project can (and should) have actions associated with it. Completing each action moves the project closer to completion:
Projects actions appear in the Next list
The Next list (key 2) combines all actionable tasks from your active projects, so that you can pick your work from a single list instead of switching between projects.
Sequential vs Parallel projects
In a sequential project only the top action is considered actionable and gets added to the Next list. In a parallel project, all next actions will appear in the Next list.
You can drag-and-drop actions within a project to specify the order in which sequential actions will appear in the Next list.
To switch the project type, click on the project’s title to open the editor view, then change the type:
When to use a Checklist vs a Project
Any item in Everdo can have a checklist as part of it’s description.
This feature works well for actions where you want to specify:
- a specific set of steps that should be followed
- criteria for completion
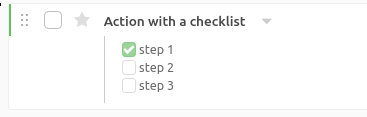
You would still like to complete such action as a whole, at once, because the checklist items don’t make sense as separate actions.
Creating a project works better when the sub-actions you need to take are distinct and self-sufficient. For example, you might do one action today and another one tomorrow. In this scenario a project is a better fit.
Converting an Action into a Project
To convert an action into a project, simply drag it to the Projects navigation section. It will then appear as one of the projects.
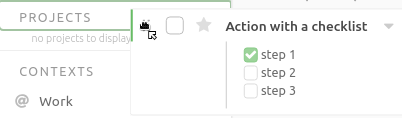
Once you’ve converted the action into a project, you can also convert it’s description into actions:
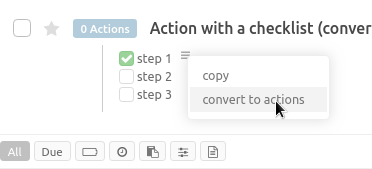
Misc Notes
- projects can have a start date and a due date
- project actions dynamically “inherit” tags from their parent project in addition to their own tags
- projects cannot be repeated on schedule
- projects can be copied (cloned) including all sub-actions by Ctrl+drag
← Back to Contents
Archival of Actions and Projects - Moved to Archive | Everdo Help
Overview
When you complete an action in Everdo, It gets moved to the Done section of the current view:
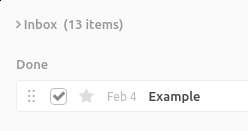
This is useful if you need to un-complete something quickly, or if you want to review what you’ve done.
But at some point you’ll have hundreds of items in Done, which is not that useful.
The purpose of the Archive feature is to hold completed items and projects forever, hiding them from Done. This reduces clutter and improves performance of the app on desktop and mobile devices.
Ways to archive
-
Drag and drop a specific action or project to the Archive navigation item

-
Archive all completed items by opening the Archive list and pressing “Move completed items to archive”.

Archive Days
Everdo keeps archived items in the database forever. But it doesn’t load everything - that would be bad for performance. There is a setting that determines the cutoff “age” of archived items that Everdo loads:
![]()
The default value is 90 days. This means that items archived over 3 months ago will not be loaded from the database. Consequently, you won’t be able to search for them or view them in the Archive list. Ninety days seems to work well most of the time, but you can modify this setting if needed (app reload required). There may be a performance benefit for using lower values, depending on the number of items you complete.
Un-Archiving
Simply move the archived item to Next or Inbox to make it active again.
Misc Notes
- Archiving an action/project automatically completes it as well
- Archiving a parent item automatically archives all it’s children
- Archived project actions remain visible in the Done list of the project. This is important to be able to see all the work that’s been done for the project.
← Back to Contents
JSON Import/Export Format - Moved to JSON Data Format | Everdo Help
 Backup you database before trying to import manually edited JSON. You could break the app by importing incomplete data, and you might not even know something is wrong until sync stops working or some weird bugs appear.
Backup you database before trying to import manually edited JSON. You could break the app by importing incomplete data, and you might not even know something is wrong until sync stops working or some weird bugs appear.
Getting Started
Make an export of your existing Everdo data to use it as an example while reading this document. This should help you understand the structure of the import objects and provide concrete examples.
Use UUID v4 for the id field
When creating new items via import, you have to generate a random universally unique id for each new item and tag. When there’s a collision, the import code silently overwrites the existing item. To avoid a collision, always use a random UUID (v4) generator when creating the import objects (unless you do want to update existing items).
List of fields using UUID data type
id-
parent_id(reference to the project’s/notebook’sid) -
contact_id(reference to the contact tag’sid)
UUID Formating
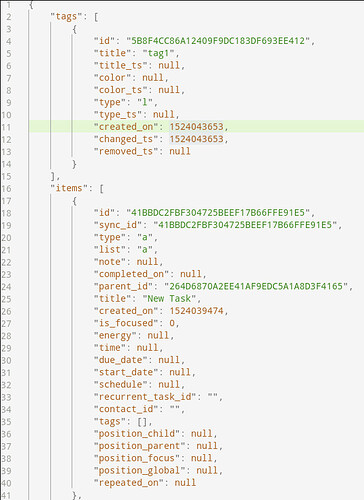
id, parent_id and other UUID fields need to be specified as an uppercase string without dashes, for example:
id: "709632E58EF74A55A18E9347F24ED948"
This is important. Other formats may cause issues.
Timestamps
All timestamps are integers, representing Unix time in seconds (Unix format). Millisecond timestamps will not work.
Root Object
The .json file you’ll import must contain a single object with two array properties - tags and items. Each array may contain zero or more elements.
{
"items": [],
"tags": []
}
Partial import works - you only need to specify the items you wish to add or update. Import does not delete missing items or tags.
Item Object Structure
These fields are required for all items:
idtypelisttitlecreated_onis_focused-
start_dateorschedulefor scheduled items.
Please note:
- Some combinations of
listandtypeare invalid. For example you can’t import an inbox project - Some
listvalues require specifying additional fields. For example in a scheduled item you also need to specify a start date.
type
-
"a": action -
"p": project -
"n": note -
"l": notebook
list - item state
-
"i": inbox (actions only) -
"a": active/next (based on item type) -
"m": someday -
"s": scheduled (must also specifystart_dateorschedulefield) -
"w": waiting -
"d": deleted -
"r": archived (must also specifycompleted_on)
completed_on
Completion timestamp (see Timestamps for format description). Null/undefined for incomplete items. Not null for completed items.
created_on
Creation timestamp. Required.
is_focused
Values: 0 or 1.
Warning: True and False will not work.
energy
Energy estimate.
Values: null, 1, 2, 3
time
Time estimate.
Value: number of minutes
due_date
Optional due date.
The timestamp’s time must be set to 0 Hours, 0 Minutes, 0 Seconds.
start_date
For one-time scheduled items only.
The timestamp’s time must be set to 0 Hours, 0 Minutes, 0 Seconds.
schedule
For repeating items only. This is a complex object. Try exporting some pre-scheduled items to get an idea how it works.
recurrent_task_id
The “template” action that was used to create an instance of this specific repeating action.
contact_id
Optional contact tag to wait for. The value is tag id.
tags
An array of tag ids. Don’t pass whole objects here, only string IDs.
position_child, position_parent, position_focus, position_global
Item’s position in a specific list:
- child: position in a list of all sub-items (project actions / notes)
- parent: position in a list of all parent items (projects/notebooks)
- focus: position in a global focus list
- global: position in a the list of all items
Examples
Examples shown here only specify all the required properties (apart from “note”, which is not required)
Inbox Action:
{
"id": "709632E58EF74A55A18E9347F24ED948" ,
"type": "a"
"title": "Example Inbox Action",
"list": "i",
"note": "optional description",
"created_on": 1549619289,
"is_focused" : 0
}
Active Project (empty)
{
"id": "B4F96775965F4F73A611365056301220" ,
"type": "p"
"title": "Example Project",
"list": "a",
"note": "optional description",
"created_on": 1549619289,
"is_focused" : 0
}
Active Project (empty)
{
"id": "709632E58EF74A55A18E9347F24ED948" ,
"type": "p"
"title": "Example Project",
"list": "a",
"note": "optional description",
"created_on": 1549619289,
"is_focused" : 0
}
Project action (active, focused)
{
"id": "B4F96775965F4F73A611365056301220" ,
"type": "a"
"list": "a",
"title": "Example Project Action",
"created_on": 1549619289,
"is_focused" : 1,
"parent_id": "709632E58EF74A55A18E9347F24ED948"
}
Tag (label) without color
{
"id": "709632E58EF74A55A18E9347F24ED948",
"title": "Example Tag",
"type": "l"
}
Ask Questions
This document only covers the very basics of Everdo JSON format. If something you need is not covered, please PM me on this forum with specific questions.
← Back to Contents
Application Directory - Moved to Data Directory | Everdo Help
Everdo stores all it’s data in the following directory.
- on Linux: ~/.config/everdo/db
- on OS X: ~/Library/Application Support/everdo/db
- on Windows: %USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\Everdo\db
Specifically,
- The application configuration file is
config.json - The sqlite3 database file will all your data is
db - The product key (for Pro users) is
everdo.key - The data encryption passphrase (used for ESS integration) is
encryption-key - The error log file is
error.log.